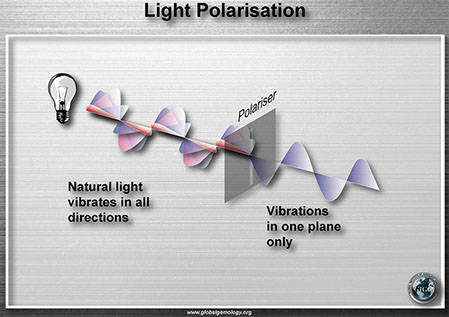

Polariscope: Principle
Polariscope: how to use it

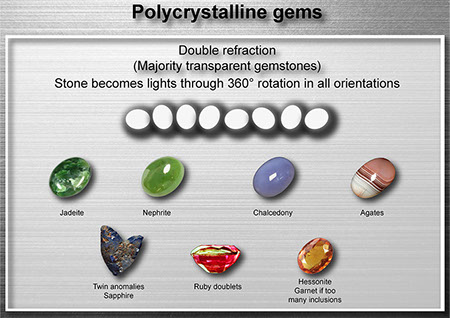
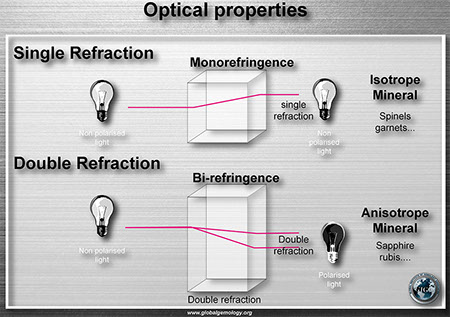
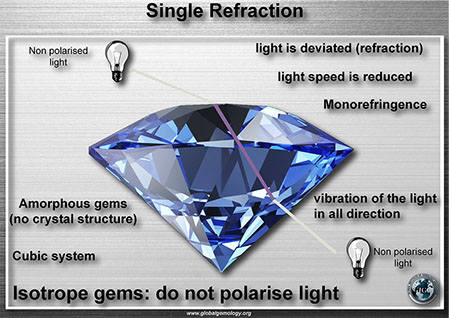
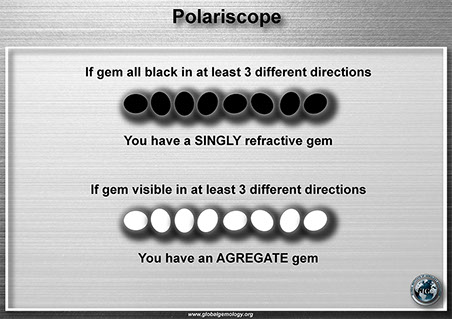
Polariscope: singly refractive and agregate gems

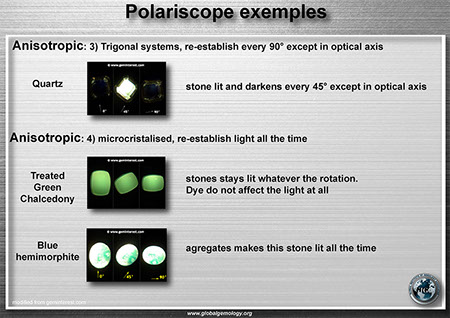
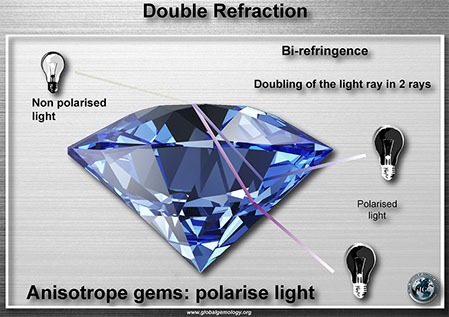
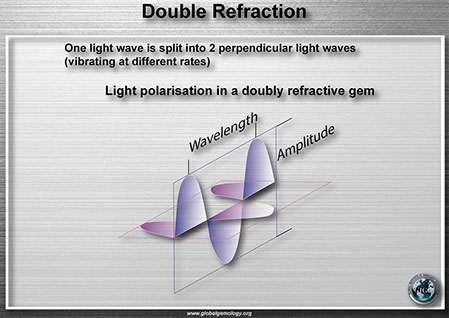
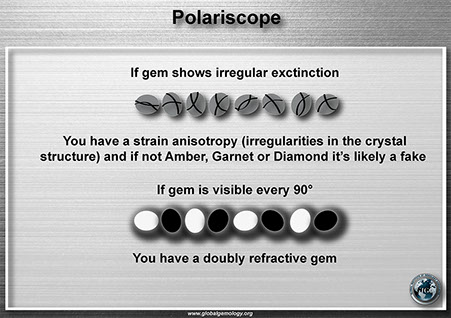
Polariscope: double refractive and strain anisotropy
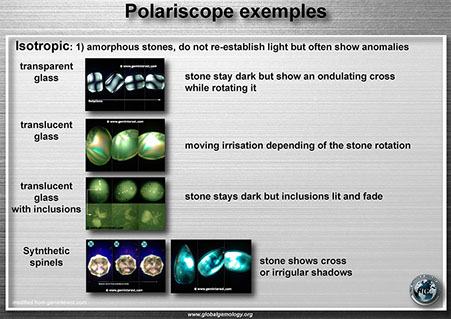
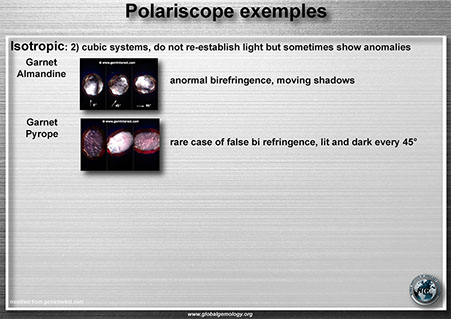
Polariscope: isotropic examples
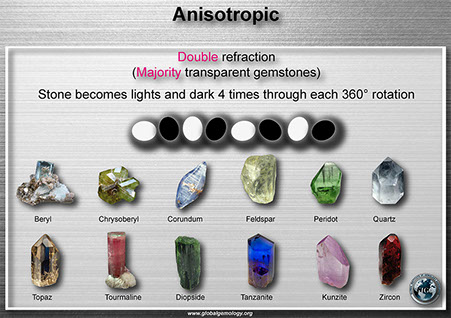
Polariscope: anisotropic examples

Polariscope: strain anistropy

Polariscope: isotropic exemples
For more information, visit: http://www.geminterest.com
For more information, visit: http://www.geminterest.com
Polariscope: isotropic exemples
and the video here: